**Geopolitical and Historical Aspects**:
– The term ‘Middle East’ originated in the 1850s and was later strategically used by Alfred Thayer Mahan.
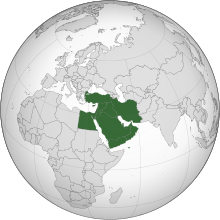
– The region encompasses the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
– Major rivers like the Nile, Tigris, and Euphrates support agriculture, while petroleum reserves are abundant in countries bordering the Persian Gulf.
– The Middle East is known for its hot, arid climate and is home to diverse ethnic groups, including Arabs, Turks, Persians, Kurds, and more.
– The Middle East has a rich history dating back to ancient times, being the birthplace of major religions and early civilizations like Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt.
**Cultural and Religious Significance**:
– Major religions like Judaism, Christianity, and Islam have origins in the Middle East.
– Arabs constitute the main ethnic group, with a diverse ethnic and religious composition in the region.
– The Middle East is a significant cultural and historical center, known as the cradle of civilization.
– The region has been a center of world affairs, strategically, economically, politically, culturally, and religiously.
– Christian communities, along with minority religions like Baháʼí Faith, Yazidism, and Zoroastrianism, play vital roles in the region.
**Geographical and Climate Characteristics**:
– The Middle East generally has a hot, arid climate, with exceptions in the Levant, Turkey, and parts of Egypt.
– The Fertile Crescent region supports agriculture, while countries in the region have varying climates.
– Countries bordering the Persian Gulf have vast petroleum reserves, contributing to the region’s economy.
– The region has a long history of advanced cultures and is geographically diverse.
– The Middle East’s geopolitical importance extends beyond its traditional boundaries.
**Modern Era and Demographics**:
– The modern Middle East emerged post-World War I, with significant events like the establishment of Israel in 1948.
– European powers left the region by the end of the 1960s, with the United States gaining influence in the following decades.
– Oil production in the Middle East started around 1945, with countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Kuwait having significant reserves.
– The Cold War saw the region as a battleground between NATO/US and the Soviet Union/Warsaw Pact.
– Migration has been significant in the region, affecting labor markets and demographics.
**Economic and Environmental Factors**:
– Middle Eastern economies vary from very poor to extremely wealthy nations, with positive growth rates reported in the past.
– Tourism is a growing industry in countries like UAE, Bahrain, and Jordan.
– The MENA region emitted a significant amount of CO2 in 2018, making it vulnerable to climate change impacts.
– IPCC projects worsening climatic conditions in the region throughout the 21st century, particularly affecting water resources.
– Over 60% of the MENA population lives in high water-stressed areas, indicating potential strains on water and agricultural resources.
The Middle East (term originally coined in English [see § Terminology]) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East (as opposed to the Far East) beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and being seen as too Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai) and all of Turkey (not just the part barring East Thrace).
 | |
| Area | 7,207,575 km2 (2,782,860 sq mi) |
|---|---|
| Population | 371 million (2010) |
| Countries | UN members (16) UN observer (1) |
| Dependencies | |
| Languages | 60 languages
|
| Time zones | UTC+02:00, UTC+03:00, UTC+03:30, UTC+04:00, UTC+04:30 |
| Largest cities | |
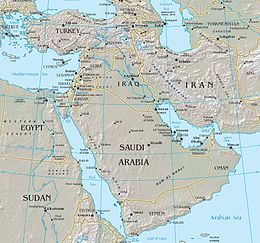

Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, while Saudi Arabia is the largest Middle Eastern country by area. The history of the Middle East dates back to ancient times, with the geopolitical importance of the region being recognized for millennia. Several major religions have their origins in the Middle East, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Arabs constitute the main ethnic group in the region, followed by Turks, Persians, Kurds, Azeris, Copts, Jews, Assyrians, Iraqi Turkmen, Yazidis, and Greek Cypriots.
The Middle East generally has a hot, arid climate, especially in the Arabian and Egyptian regions. Several major rivers provide irrigation to support agriculture in limited areas here, such as the Nile Delta in Egypt, the Tigris and Euphrates watersheds of Mesopotamia, and the basin of the Jordan River that spans most of the Levant. These regions are collectively known as the Fertile Crescent, and comprise the core of what historians had long referred to as the cradle of civilization (a label now applied to multiple regions of the world). Conversely, the Levantine coast and most of Turkey have relatively temperate climates typical of the Mediterranean, with dry summers and cool, wet winters. Most of the countries that border the Persian Gulf have vast reserves of petroleum, with monarchs of the Arabian Peninsula in particular benefiting economically from petroleum exports. Because of the arid climate and heavy reliance on the fossil fuel industry, the Middle East is both a heavy contributor to climate change and a region expected to be severely negatively impacted by it.
Other concepts of the region exist including the broader Middle East and North Africa (MENA), which includes states of the Maghreb and the Sudan, or the "Greater Middle East" which additionally also includes parts of East Africa, Mauritania, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and sometimes the South Caucasus and Central Asia.
