**Historical Development of Ancient Egypt:**
– Nile River as a lifeline for settlements and agriculture
– Evolution from hunter-gatherer societies to centralized kingdoms
– Predynastic Period with early tribes and cultures like Badarian and Naqada
– Transition to a unified state in the Early Dynastic Period
– Achievements in architecture, mathematics, medicine, and technology
**Political History and Dynastic Periods:**
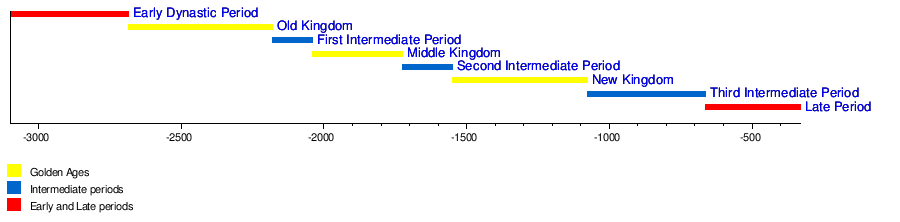
– Division of history into dynastic periods by Egyptian priest Manetho
– Old Kingdom with major architectural advancements like the pyramids
– Periods of instability like the First Intermediate Period
– Restoration of stability in the Middle Kingdom
– Conquests and foreign influences in the New Kingdom
**Social Structure and Legal System:**
– Highly stratified society with distinct classes
– Equality of men and women under ancient Egyptian law
– Legal system based on common-sense views of right and wrong
– Importance of maintaining Maat, the concept of justice
– Use of oracles in the legal system for dispensing justice
**Economy and Agriculture:**
– Centralized economy with a barter system and fixed prices
– Three agricultural seasons based on the Nile’s flooding
– Crops grown including grains, flax, and papyrus
– Role of temples in collecting and redistributing wealth
– Utilization of natural resources like stone, ores, and salts
**Later Periods and Foreign Rule:**
– Roman conquest and Egypt becoming a Roman province
– Influence of Christianity in Egypt during the Roman period
– Establishment of the Ptolemaic Kingdom by Alexander the Great
– Challenges faced by the Ptolemies from native rebellions
– Transition from native dynasties to Roman rule and subsequent history
Ancient Egypt was a civilization of ancient Northeast Africa. It was concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River, situated in the place that is now the country Egypt. Ancient Egyptian civilization followed prehistoric Egypt and coalesced around 3100 BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology) with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under Menes (often identified with Narmer). The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by periods of relative instability known as “Intermediate Periods.” The various kingdoms fall into one of three categories: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age, or the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age.
Ancient Egypt | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
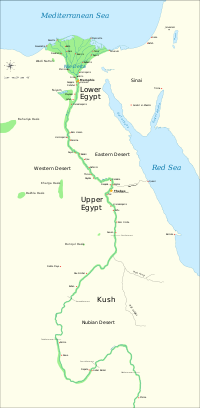 Map of ancient Egypt, showing major cities and sites of the Dynastic period (c. 3150 BC to 30 BC) | |||||||||
| |||||||||
Ancient Egypt reached the pinnacle of its power during the New Kingdom, ruling much of Nubia and a sizable portion of the Levant. After this period, it entered an era of slow decline. During the course of its history, Ancient Egypt was invaded or conquered by a number of foreign powers, including the Hyksos, the Nubians, the Assyrians, the Achaemenid Persians, and the Macedonians under Alexander the Great. The Greek Ptolemaic Kingdom, formed in the aftermath of Alexander's death, ruled until 30 BC, when, under Cleopatra, it fell to the Roman Empire and became a Roman province. Egypt remained under Roman control until the 640s AD, when it was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate.
The success of ancient Egyptian civilization came partly from its ability to adapt to the conditions of the Nile River valley for agriculture. The predictable flooding and controlled irrigation of the fertile valley produced surplus crops, which supported a more dense population, and social development and culture. With resources to spare, the administration sponsored mineral exploitation of the valley and surrounding desert regions, the early development of an independent writing system, the organization of collective construction and agricultural projects, trade with surrounding regions, and a military intended to assert Egyptian dominance. Motivating and organizing these activities was a bureaucracy of elite scribes, religious leaders, and administrators under the control of a pharaoh, who ensured the cooperation and unity of the Egyptian people in the context of an elaborate system of religious beliefs.
The many achievements of the ancient Egyptians include the quarrying, surveying, and construction techniques that supported the building of monumental pyramids, temples, and obelisks; a system of mathematics, a practical and effective system of medicine, irrigation systems, and agricultural production techniques, the first known planked boats, Egyptian faience and glass technology, new forms of literature, and the earliest known peace treaty, made with the Hittites. Ancient Egypt has left a lasting legacy. Its art and architecture were widely copied, and its antiquities were carried off to far corners of the world. Its monumental ruins have inspired the imaginations of travelers and writers for millennia. A newfound respect for antiquities and excavations in the early modern period by Europeans and Egyptians has led to the scientific investigation of Egyptian civilization and a greater appreciation of its cultural legacy.