**Types of Hypoxia:**
– Atmospheric Hypoxia:
– Occurs naturally at high altitudes
– Total atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude
– Lower partial pressure of oxygen at high altitudes
– Oxygen remains at 20.9% of the total gas mixture
– Basis of altitude training for elite athletes
– Aquatic Hypoxia:
– Anoxic aquatic systems lack dissolved oxygen
– Oxygen levels in water are approximately 7 ppm
– Hypoxic conditions are required by many organisms
– Most fish cannot live below 30% oxygen saturation
– Healthy aquatic environments should rarely have less than 80% oxygen saturation
**Causes and Effects of Hypoxia:**
– Causes of Hypoxia:
– Oxygen depletion can result from natural factors
– Pollution and eutrophication are common causes
– Phytoplankton blooms can lead to oxygen depletion
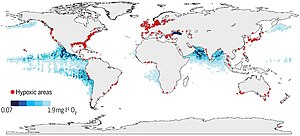
– Dead zones can be created in estuaries
– Hypoxic coastal zones are a global concern
– Seasonal Kill:
– Hypolimnetic oxygen depletion leads to summer and winter kills
– Summer kills occur due to extreme oxygen depletion
– Winter kills happen when ice cover reduces oxygen exchange
– Anaerobic organisms can die in winter kills
– Hypoxia can extend throughout the water column
**Phytoplankton and Oxygen Consumption:**
– Phytoplankton Breakdown:
– Phytoplankton breakdown consumes oxygen
– Oxygen presence affects breakdown rate
– Rate of breakdown can be represented by an equation
– Oxygen is used up quickly in the breakdown process
– Breakdown releases dissolved carbon into the environment
**Environmental Impact and Concerns:**
– Algal blooms
– Anoxic event
– Dead zone (ecology)
– Cyanobacterial bloom
– Denitrification
– Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters
– Ocean time series observations of changing marine ecosystems
– Spreading Dead Zones and Consequences for Marine Ecosystems
– Aquatic Hypoxia Is an Endocrine Disruptor and Impairs Fish Reproduction
– Characterization of Hypoxia: Topic 1 Report for the Integrated Assessment on Hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico
**Research and Studies on Hypoxia:**
– Dissolved Oxygen
– Encyclopedia of Puget Sound: Hypoxia
– Modeling the biodegradation of multicomponent organic matter in an aquatic environment
– Dynamics and impact of ocean acidification and hypoxia
– Oceanography: Dead in the water
– Environmental conditions in burrows of two species of African mole-rat
– Limnology: Lake and river ecosystems
– Eutrophication: An Overview of Status, Trends, Policies, and Strategies
– Dead Zone Causing a Wave of Death Off Oregon Coast
– Kinetics of phytoplankton decay during simulated sedimentation
– In situ Investigations on Respiration and Behaviour of Stickleback and the Eelpout During Low Oxygen Stress
– In situ investigations on the respiration and behaviour of the eelpout under short term hypoxia
Hypoxia refers to low oxygen conditions. For air-breathing organisms, hypoxia is problematic but for many anaerobic organisms, hypoxia is essential. Hypoxia applies to many situations, but usually refers to the atmosphere and natural waters.