**Hydrates**:
– Sodium carbonate exists in three hydrates (decahydrate, heptahydrate, monohydrate) and as an anhydrous salt.
– Anhydrous sodium carbonate is obtained by heating the hydrates.
– Different hydrates form at specific temperature ranges.
– Other hydrates with varying water content have been reported.
**Washing Soda**:
– Sodium carbonate decahydrate, known as washing soda, contains 10 molecules of water.
– Obtained by dissolving soda ash in water and crystallizing.
– It is one of the few metal carbonates soluble in water.
**Applications**:
– Used in cleansing agents, dry soap powders, glass, soap, and paper manufacturing.
– Lowers water hardness and aids in producing sodium compounds like borax.
**Glass Manufacture**:
– Acts as a flux for silica, reducing the melting point.
– Added to soda–lime glass production to make glass insoluble.
**Production**:
– **Mining**: Trona mined in the US, large deposits near Green River, Wyoming, important reserves in Turkey.
– **Barilla and Kelp**: Historical sources from halophyte plants and seaweed.
– **Leblanc Process**: Developed in 1792 for sodium carbonate production, dominated until late 1880s.
– **Hou’s Process**: Developed in the 1930s, coupled to the Haber process for better atom economy.
– Various sources and studies on the production methods.
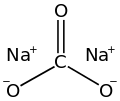
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils, and because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the Chlor-alkali process.
| |

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium carbonate
| |
| Other names
Soda ash, washing soda, soda crystals, sodium trioxocarbonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.127 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E500(i) (acidity regulators, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Na2CO3 | |
| Molar mass | 105.9888 g/mol (anhydrous) 286.1416 g/mol (decahydrate) |
| Appearance | White solid, hygroscopic |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density |
|
| Melting point | 851 °C (1,564 °F; 1,124 K) (Anhydrous) 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) decomposes (monohydrate) 33.5 °C (92.3 °F; 306.6 K) decomposes (heptahydrate) 34 °C (93 °F; 307 K) (decahydrate) |
Anhydrous, g/100 mL:
| |
| Solubility | Soluble in aq. alkalis, glycerol Slightly soluble in aq. alcohol Insoluble in CS2, acetone, alkyl acetates, alcohol, benzonitrile, liquid ammonia |
| Solubility in glycerine | 98.3 g/100 g (155 °C) |
| Solubility in ethanediol | 3.46 g/100 g (20 °C) |
| Solubility in dimethylformamide | 0.5 g/kg |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.33 |
| −4.1·10−5 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.485 (anhydrous) 1.420 (monohydrate) 1.405 (decahydrate) |
| Viscosity | 3.4 cP (887 °C) |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic (γ-form, β-form, δ-form, anhydrous) Orthorhombic (monohydrate, heptahydrate) | |
| C2/m, No. 12 (γ-form, anhydrous, 170 K) C2/m, No. 12 (β-form, anhydrous, 628 K) P21/n, No. 14 (δ-form, anhydrous, 110 K) Pca21, No. 29 (monohydrate) Pbca, No. 61 (heptahydrate) | |
| 2/m (γ-form, β-form, δ-form, anhydrous) mm2 (monohydrate) 2/m 2/m 2/m (heptahydrate) | |
a = 8.920(7) Å, b = 5.245(5) Å, c = 6.050(5) Å (γ-form, anhydrous, 295 K) α = 90°, β = 101.35(8)°, γ = 90°
| |
| Octahedral (Na+, anhydrous) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
112.3 J/mol·K |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
135 J/mol·K |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1130.7 kJ/mol |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−1044.4 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
4090 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Sodium bicarbonate |
Other cations
|
Lithium carbonate Potassium carbonate Rubidium carbonate Cesium carbonate |
Related compounds
|
Sodium sesquicarbonate Sodium percarbonate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

